Euroregions[1] are specific areas of cross-border regional cooperation in Europe. They are set up to promote economic development (e.g. border infrastructure construction) and to jointly solve local problems of a cross-border nature (e.g. environmental protection and restoration). They also create the conditions for diverse interpersonal contacts of a cultural, sporting and scientific nature.
In Western Europe, the first Euroregions were created from the late 1950s, and in Central and Eastern Europe, after the political changes, from the 1990s.
There are 17 euroregions within Poland.
|
Euroregion |
Year of establishment |
Members |
|
Nysa |
1991 |
Poland, Czechia, Germany |
|
Carpathian |
1993 |
Poland, Slovakia, Ukraine, Hungary, Romania |
|
Sprewa-Nysa-Bóbr |
1993 |
Poland, Germany |
|
Pro Europa Viadrina |
1993 |
Poland, Germany |
|
Tatry |
1994 |
Poland, Slovakia |
|
Bug |
1995 |
Poland, Ukraine, Belarus |
|
Pomerania |
1995 |
Poland, Germany |
|
Glacensis |
1996 |
Poland, Czechia |
|
Niemen |
1997 |
Poland, Lithuania, Belarus, Russia |
|
Praded |
1997 |
Poland, Czechia |
|
Baltic |
1998 |
Poland, Russia, Lithuania, Sweden, Danemark |
|
Cieszyn-Český Těšín |
1998 |
Poland, Czechia |
|
Silesia |
1998 |
Poland, Czechia |
|
Beskydy (Beskidy) |
2000 |
Poland, Czechia, Slovakia |
|
Białowieska Forest |
2002 |
Poland, Belarus |
|
Łyna-Ława |
2003 |
Poland, Russia |
|
Roztocze |
2020 |
Poland, Ukraine |
The development of Euroregions, and thus cross-border cooperation, is financially supported by EU Community initiatives as it forms an important part of the EU’s regional development policy.
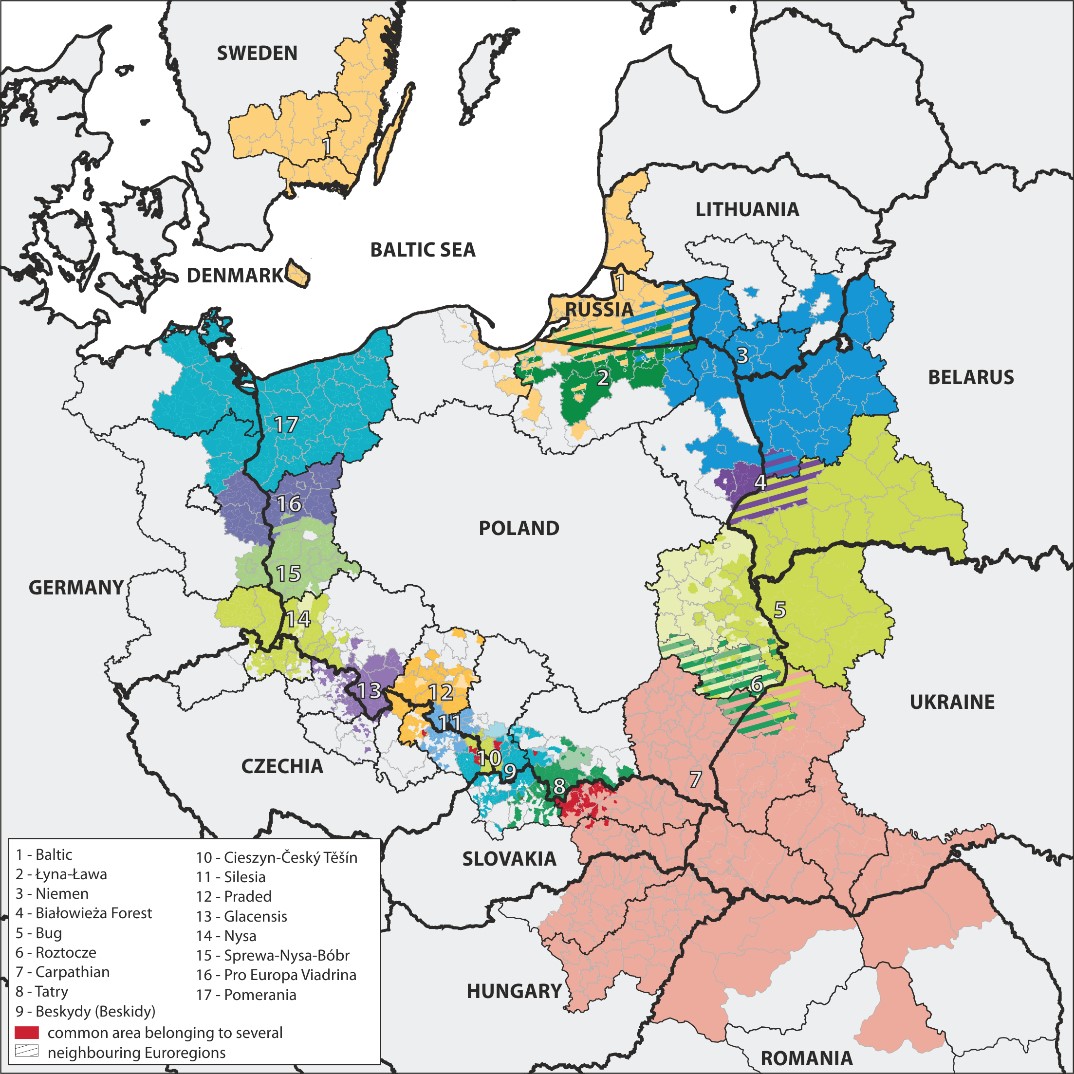
The Nysa Euroregion was established in December 1991. It covers the areas located at the corner of Polish borders (areas of the Western Sudetes and Żarski powiat), Czechia (areas of the Western Sudetes and the Usti nad Labem region) and Germany (from the Lusatian Mountains and the Lusatian Foothills to the north, including also Lower Lusatia, powiats of Löbau – Żytawa, Budziszyn, Kamenz, Upper Lusatia – Lower Silesia).
The Carpathian Euroregion was established in February 1993. An agreement on creation of the Interregional Union „Carpathian Euroregion” was signed by the representatives of regional authorities: Poland, Slovakia, Ukraine and Hungary. The Romanian side was accepted as a member in April 1997. The Carpathian Euroregion is the largest Euroregion on the Polish border in terms of area.
The Sprewa-Nysa-Bóbr Euroregion was established in September 1993. On the Polish side, it covers the southern and central part of Lubuskie Voivodship and Zbąszyń gmina, which belongs to Wielkopolskie Voivodship. On the German side, the Euroregion includes the Spree-Nysa powiat and the city of Cottbus. Over 50% of the Euroregion’s area is covered by forests.
The Pro Europa Viadrina Euroregion was established in December 1993. It is located in the northern part of Lubuskie Voivodship on the Polish side and in the east of the Federal State of Brandenburg on the German side. The sense and purpose of creating this Euroregion was already revealed in its name. The literal translation of this name from Latin means „to Europe via the Oder”. The idea was to unite Eastern and Western Europe and this term corresponds to the slogan: „For Europe on the Oder”.
The Tatry Euroregion was established in August 1994. Members of the Cross-Border Euroregion Association „Tatry” are local government units of the Polish-Slovak border. The Slovak part of the Tatra Euroregion lies in the northern part of Slovakia and covers the historical regions of: Spisz, Liptov, Orava and part of Szarisz. On the Polish side, it covers the area of gminas and cities located in the area of 7 powiats of Małopolskie Voivodship.
The Bug Euroregion was established in September 1995, founded by representatives of Poland and Ukraine, and three years later it was extended to the territory of Belarus. It covers the areas located in the catchment area of the Bug River. It consists of Lubelskie Voivodship in Poland, the Brzeski Oblast in Belarus, Volyn Oblast and two districts from Lviv Oblast in Ukraine.
The Pomerania Euroregion was established in December 1995. An agreement on its establishment was signed by representatives of Poland and Germany. In February 1998 a declaration was signed in Lund, Sweden, for the Union of Skåne Municipalities to join Euroregion Pomerania. In March 2013, due to a difficult financial situation, the Union of Skåne Municipalities withdrew from the Pomerania Euroregion.
The Glacensis Euroregion was established in December 1996. The Framework Agreement between the association of towns and municipalities of the district of Kłodzko and the Regional Association for Cooperation on the Borderland of Czechia, Moravia and the Kłodzko district was signed. The name of this Euroregion has a historical origin and comes from the Medieval Latin term for the Kłodzko Valley.
The Niemen Euroregion was established in June 1997. Its founders were: former Suwałki voivodship (Poland), Alytus and Marijampole voivodships (Lithuania) and Grodno region (Belarus). In April 2002 the Russian side joined the Euroregion.
The Praded Euroregion was established in July 1997. The idea of the Euroregion foundation was the rapprochement and cooperation between Poland and Czechia on the border of Moravia, Silesia and Opole Silesia. The name comes from the highest mountain peak in the area (Praded – 1491 m).
The Baltic Euroregion was established in February 1998 and is an organisation based on the cooperation of the south-eastern part of the Baltic Sea region. It consists of regions from: Denmark, Lithuania, Poland, Russia and Sweden.
The Cieszyn-Český Těšín Euroregion was established in April 1998. It is located on the border area of southern Poland and north-eastern Czechia, in the close neighbourhood of Slovakia. The Euroregion area stretches from Godów and Jastrzębie-Zdrój to Istebna, and from Bohumin to Hrčavu. The natural axis of this area is the Olza River.
The Silesia Euroregion was established in September 1998. The Polish part of the Silesia Euroregion is formed by the Polish Association of Municipalities of the Upper Oder River. The capital city of the Silesia Euroregion on the Polish side is Racibórz. The Czech part of the Silesia Euroregion was created by the Regional Association for the Czech-Polish Cooperation Opavian Silesia, now called Euroregion Silesia-CZ. The capital of the Silesia Euroregion on the Czech side is the town of Opava.
The Beskydy (Beskidy) Euroregion was established in June 2000 on the initiative of local authorities of Beskydy mountain communities from the Polish-Slovakian-Czech border. It consists of three associations based in: Poland, Czechia and Slovakia.
The Białowieża Forest Euroregion was established in May 2002. The Polish part of the Euroregion Białowieża Primeval Forest is located in the south-eastern part of Podlaskie Voivodship. The Belarusian part is located in the western part of Belarus. These are neighbouring regions encompassing – unique in Europe and in the world – the primeval forest complex of the Białowieża Primeval Forest.
The Łyna-Ława Euroregion was established in September 2003. It is an international association of local authorities from Warmińsko-Mazurskie Voivodship (Polish side) and the Kaliningrad Oblast (Russian side). It is based in Bartoszyce in Poland.
The Roztocze Euroregion was established in November 2020 on the basis of an agreement between the Association of Local Governments Euroregion Roztocze (Polish side) and the Association of Local Governments Roztocze Euroregion Ukraine. As a result of signing the agreement the Cross-Border Union Roztocze Euroregion was established. The Roztocze Euroregion comprises directly neighbouring areas of Poland and Ukraine, including in particular the Roztocze UNESCO Cross-Border Biosphere Reserve and adjacent areas.
Selected data on Euroregions on the Polish border in the years 2020–2022
|
Euroregion |
Population in million persons |
Area in thousand km2 |
Population per 1 km2 |
Natural increase per 1000 population |
||||||||
|
2020 |
2021 |
2022 |
2020 |
2021 |
2022 |
2020 |
2021 |
2022 |
2020 |
2021 |
2022 |
|
|
Nysa |
1.5 |
1.5 |
1.5 |
11.8 |
11.8 |
11.8 |
127.2 |
125.1 |
124.8 |
-6.8 |
-8.2 |
-7.0 |
|
Carpathian |
15.0 |
14.8 |
b.d. |
161.1 |
161.1 |
161.1 |
92.8 |
92.2 |
b.d. |
-3.9 |
-5.7 |
b.d. |
|
Sprewa-Nysa-Bóbr |
0.8 |
0.8 |
0.8 |
9.9 |
9.9 |
9.9 |
84.2 |
82.7 |
82.5 |
-5.2 |
-6.8 |
-6.0 |
|
Pro Europa Viadrina |
0.8 |
0.8 |
0.8 |
10.7 |
10.7 |
10.7 |
76.4 |
75.7 |
76.1 |
-5.5 |
-7.2 |
-6.9 |
|
Tatry |
0.9 |
0.8 |
0.8 |
6.9 |
6.9 |
6.9 |
124.0 |
122.2 |
122.0 |
1.1 |
-0.6 |
0.5 |
|
Bug |
4.7 |
4.6 |
b.d. |
80.9 |
80.9 |
80.9 |
57.7 |
56.8 |
b.d. |
-3.7 |
-5.2 |
b.d. |
|
Pomerania |
2.7 |
2.7 |
2.7 |
40.1 |
40.1 |
40.1 |
67.6 |
66.7 |
66.7 |
-5.4 |
-7.4 |
-7.2 |
|
Glacensis |
0.8 |
0.8 |
0.8 |
5.8 |
5.8 |
5.8 |
133.5 |
129.2 |
128.9 |
-6.6 |
-9.0 |
-7.1 |
|
Niemen |
2.7 |
2.7 |
2.7 |
53.8 |
53.8 |
53.8 |
50.3 |
49.9 |
49.8 |
-4.3 |
-5.6 |
b.d. |
|
Praded |
0.8 |
0.8 |
0.8 |
7.4 |
7.4 |
7.4 |
107.3 |
104.3 |
103.1 |
-4.9 |
-6.5 |
-5.1 |
|
Baltic |
3.4 |
3.4 |
3.4 |
49.2 |
49.1 |
49.1 |
69.0 |
69.4 |
69.4 |
-3.1 |
-4.7 |
-4.0 |
|
Cieszyn-Český Těšín |
0.6 |
0.6 |
0.6 |
1.7 |
1.7 |
1.7 |
362.3 |
357.7 |
357.9 |
-4.1 |
-5.9 |
-4.0 |
|
Silesia |
0.8 |
0.7 |
0.7 |
2.8 |
2.8 |
2.8 |
275.1 |
268.8 |
268.8 |
-3.9 |
-5.1 |
-4.3 |
|
Beskydy (Beskidy) |
1.4 |
1.4 |
1.4 |
6.3 |
6.3 |
6.3 |
224.2 |
222.8 |
222.7 |
-1.8 |
-3.7 |
-2.5 |
|
Białowieża Forest |
0.1 |
0.1 |
0.1 |
8.2 |
8.2 |
8.2 |
17.4 |
16.8 |
16.5 |
-11.3 |
-13.1 |
b.d. |
|
Łyna-Ława |
0.6 |
0.5 |
0.5 |
14.2 |
14.2 |
14.2 |
39.3 |
38.5 |
38.3 |
-3.9 |
-6.3 |
b.d. |
|
Roztocze |
0.8 |
0.8 |
b.d. |
11.3 |
11.3 |
11.3 |
69.0 |
67.1 |
b.d. |
b.d. |
b.d. |
b.d. |
b.d. – data not available.
EUROREGIONS:
Nysa https://www.euroregion-nysa.pl/
Carpathian https://www.karpacki.pl/
Sprewa-Nysa-Bóbr http://euroregion-snb.pl/
Pro Europa Viadrina https://www.euroregion-viadrina.pl/
Tatry http://www.euroregion-tatry.pl
Pomerania https://www.pomerania.org.pl/
Glacensis http://euroregion-glacensis.ng.pl/
Niemen https://niemen.org.pl/
Praded https://europradziad.pl/
Baltic https://eurobalt.org.pl/
Cieszyn-Český Těšín https://www.olza.pl/pl/o-nas/euroregion-slask-cieszynski/
Silesia https://euroregion-silesia.pl/
Beskydy (Beskidy) http://www.euroregion-beskidy.pl/
Białowieża Forest http://www.euroregion-pb.pl/wordpress/
Łyna-Ława http://encyklopedia.warmia.mazury.pl/index.php/Euroregion_Łyna-Ława
Roztocze https://euroregionroztocze.org.pl/
[1] https://encyklopedia.pwn.pl/haslo/euroregiony;3899216.html (access 10.03.2025).
